
Blockchain technology has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation that is revolutionizing the way transactions are conducted in the digital realm. At its core, blockchain is a transaction technology that enables the transfer of digital assets with remarkable similarities to physical transactions. The key features of blockchain, such as instantaneity, verifiability, peer-to-peer interactions, and the elimination of the need for trusted intermediaries, provide a new level of trust and security in the digital world.
One of the most notable applications of blockchain technology is seen in Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency that allows users to replicate the user experience of physical cash in the digital realm. Just as physical cash can be exchanged without the need for intermediaries, Bitcoin transactions occur directly between parties, ensuring fast, secure, and transparent transactions.
However, the potential of blockchain technology extends far beyond cryptocurrency and money. Virtually every industry, including financial services, healthcare, supply chain, retail, and the food industry, can benefit from the application of blockchain technology. By harnessing the power of blockchain, various asset classes can be securely transferred and tracked, providing unprecedented transparency and efficiency in business processes.
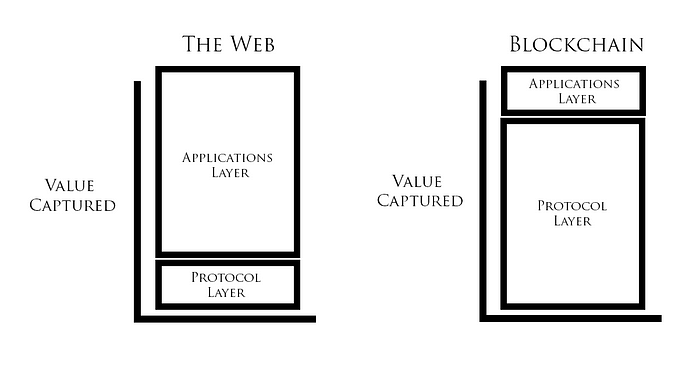
It is important to understand that blockchain is not just a platform; rather, it is a protocol. This means that the true value lies within the underlying protocol layer, rather than the applications built on top of it ( Fat Protocol and Thin Application thesis). This distinction allows for greater flexibility and scalability, as multiple applications can utilize the same underlying blockchain infrastructure.
Ultimately, blockchain represents a paradigm shift in the way we design and implement economic systems. By introducing decentralized, trustless, and transparent mechanisms, blockchain technology has the potential to reshape traditional models, enhance security, and unlock new possibilities for innovation across various industries.
In this blog post, we will delve deeper into the fascinating world of blockchain technology and explore its analogy with the transfer of assets in the physical world. By examining the core principles, real-world applications, and the transformative impact of blockchain, we aim to provide valuable insights for those interested in understanding and harnessing the power of this revolutionary technology. Let’s embark on this journey of discovery and unravel the potential of blockchain as a game-changer in our digital age.
Exploring the Digital Frontier: Understanding the Age of Avatar
In the Age of Avatar, the convergence of the physical and digital realms is reshaping our understanding of assets and transactions. Blockchain technology, with its revolutionary capabilities, plays a pivotal role in this transformation by enabling the digitization of physical assets and the seamless transfer of digital assets. It establishes a powerful analogy between the transfer of assets in the physical world and the transfer of digital assets on the blockchain, offering a compelling vision of a decentralized and transparent future.
In the physical world, assets such as money, real estate, or valuable goods are transferred from one person to another through various mechanisms, involving intermediaries, paperwork, and trust. Similarly, blockchain technology allows for the transfer of digital assets in a peer-to-peer manner, eliminating the need for intermediaries and creating a trustless environment. This analogy is powerful because it demonstrates how blockchain technology can replicate the experience of physical asset transfer while adding security, efficiency, and accessibility.
Just as physical assets require verification and proof of ownership, blockchain technology ensures trust and verifiability in the transfer of digital assets. Through the use of cryptographic techniques, each transaction on the blockchain is recorded in a transparent and immutable manner, creating a permanent digital footprint. This establishes an unalterable record of ownership, facilitating the authentication and verification of digital assets. This analogy between the physical world and the blockchain highlights the crucial aspect of trust and verifiability, which are essential in both realms.
Furthermore, the instantaneous nature of blockchain transactions mirrors the speed at which physical assets can be transferred. In the physical world, immediate transactions are often limited by geographical constraints, intermediary processes, and settlement times. However, with blockchain technology, digital assets can be transferred instantly, regardless of geographical location or traditional banking hours. This analogy underscores the potential for blockchain technology to accelerate the pace of digital transactions, unlocking new possibilities for commerce and financial services.
Moreover, the transparency inherent in blockchain technology aligns with the desire for transparency in the physical world. In the physical realm, we rely on various mechanisms, such as labels, certifications, and tracking systems, to ensure the authenticity and quality of products or assets. Similarly, on the blockchain, every transaction is recorded transparently, allowing users to access the entire transaction history of a digital asset. This transparency fosters trust and enables users to verify the providence, authenticity, and attributes of digital assets, just as we do in the physical world.
The analogy between blockchain technology and the transfer of assets in the physical world is compelling because it demonstrates how blockchain can revolutionize digital transactions while capturing the essence of the physical experience. It showcases the potential of blockchain technology to bridge the gap between these two realms and create a more secure, efficient, and transparent digital ecosystem. As we continue to explore the possibilities of the Age of Avatar, blockchain technology stands as a transformative force, enabling us to embrace the benefits of both the physical and digital worlds in harmony.
The Role of Blockchain in Digitizing Physical Assets
Blockchain technology plays a vital role in digitizing physical assets, providing a secure and transparent environment for their representation and transfer. By tokenizing physical assets on the blockchain, they are transformed into digital tokens with unique identifiers and ownership records. These digital tokens can then be bought, sold, or traded, much like physical assets in the physical world. The analogy here is that blockchain allows us to transfer ownership of digital representations of physical assets in a way that closely mimics physical transactions, but with added benefits such as enhanced security and immutability.
Here are few examples that demonstrate the role of blockchain in digitizing physical assets:
Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain technology can greatly enhance transparency and traceability in supply chains by digitizing physical assets. For instance, IBM Food Trust utilizes blockchain to track the journey of food products from farm to store shelves. By capturing and recording each step of the supply chain on the blockchain, stakeholders can verify the origin, quality, and safety of products, reducing fraud and ensuring consumer trust.
Real Estate Tokenization: Blockchain enables the digitization and fractional ownership of physical real estate assets. Platforms like RealT and Propy leverage blockchain to tokenize real estate properties, representing ownership as digital tokens. These tokens can be easily bought, sold, and traded, unlocking liquidity and enabling smaller investors to participate in the real estate market. Blockchain’s immutability ensures transparent and secure property ownership records.
Digital Identity Verification: Blockchain technology can streamline the process of verifying and managing digital identities, enhancing security and privacy. SelfKey is an example of a blockchain-based digital identity network that allows individuals to securely store and control their personal identity information. By leveraging cryptography and decentralized storage, SelfKey enables users to authenticate their identity without relying on centralized authorities, reducing the risk of data breaches and identity theft.
Digital Securities and Tokenization: Blockchain enables the tokenization of physical assets, including securities such as stocks, bonds, and commodities. Platforms like tZERO provide a secure and transparent environment for issuing, trading, and settling digital securities. By tokenizing traditional financial assets, blockchain technology allows for fractional ownership, increased liquidity, and streamlined settlement processes.
Cross-Border Payments and Remittances: Blockchain-based platforms are transforming cross-border payments and remittances by digitizing the transfer of physical assets, such as money. RippleNet and Stellar are examples of networks that leverages blockchain technology to enable fast, secure, and cost-effective international money transfers. By eliminating intermediaries and utilizing digital tokens, blockchain-powered payment solutions reduce transaction fees, improve settlement speed, and enhance transparency.
These examples demonstrate how blockchain technology plays a crucial role in digitizing physical assets, offering benefits such as enhanced transparency, fractional ownership, secure data management, and improved accessibility. By leveraging blockchain’s capabilities, industries can unlock new opportunities and transform traditional asset management processes.

Securing Digital Transactions: How Blockchain Ensures Trust and Verifiability
One of the key features of blockchain technology is its ability to secure digital transactions, ensuring trust and verifiability. In the physical world, we rely on various mechanisms such as signatures, stamps, and notaries to validate transactions and establish trust between parties. Similarly, blockchain utilizes cryptographic techniques to secure digital transactions, making them tamper-proof and resistant to fraud. The decentralized nature of blockchain, where transactions are verified and recorded by multiple participants, adds an extra layer of trust and transparency, analogous to how physical transactions involve multiple parties for verification.
Here are few real world examples in the financial services industry :
Trade Finance and Letters of Credit: Traditionally, trade finance transactions involving letters of credit require extensive documentation and manual verification processes. Blockchain platforms like Marco Polo are revolutionizing this process by digitizing the exchange of trade documents on a shared, secure blockchain. This improves trust and verifiability by allowing all involved parties, including banks and traders, to access and validate the transaction data in real-time, reducing the risk of fraud and improving efficiency.
Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance: Compliance with KYC and AML regulations is essential in the financial industry to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing. Blockchain-based solutions like Jumio use distributed ledger technology to securely store and share customer identity information among financial institutions. This streamlines the onboarding process and enhances trust and verifiability by ensuring the authenticity of customer data while maintaining privacy and data protection.
Securities Settlement and Clearing: Blockchain is transforming securities settlement and clearing processes by improving transparency, reducing counterparty risk, and increasing operational efficiency. For example, Nasdaq’s Linq platform utilizes blockchain technology to facilitate the issuance, transfer, and management of private securities. By recording and verifying transactions on the blockchain, participants can securely and transparently settle securities, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the settlement time from days to minutes.
These real-world examples showcase how blockchain technology plays a vital role in securing digital transactions within the financial services industry. By providing transparency, immutability, and decentralized verification, blockchain ensures trust and verifiability while reducing fraud, improving compliance, and enhancing operational efficiency.
Blockchain’s Impact on Financial Services: Revolutionizing Transactions and Asset Management
The impact of blockchain on financial services is profound, as it revolutionizes transactions and asset management, much like physical transactions in the financial world. At its core, blockchain technology is designed to facilitate secure and transparent exchanges of value, mirroring the trust and reliability found in physical transactions. By leveraging decentralized networks and cryptographic principles, blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries and enables direct peer-to-peer transfers of assets.
In the traditional financial system, intermediaries such as banks, clearinghouses, and brokers play a crucial role in facilitating transactions. However, these intermediaries introduce complexities, delays, and costs to the process. Blockchain technology disrupts this model by enabling direct asset transfers between parties, much like handing physical cash from one person to another. This elimination of intermediaries not only reduces costs associated with transaction fees and processing, but it also significantly increases the speed and efficiency of financial transactions.
Analogous to physical contracts that govern transactions in the traditional financial system, blockchain introduces the concept of smart contracts. These self-executing agreements are encoded with predefined rules and conditions, triggering automatic actions when those conditions are met. Smart contracts streamline processes such as asset transfers, lending, and trade settlements, much like physical contracts govern the transfer of ownership or the fulfillment of obligations.
The analogy between blockchain technology and the transfer of assets in the physical world becomes even more compelling when considering the transparency and immutability of blockchain transactions. Just as physical transactions leave a traceable paper trail, blockchain transactions are recorded on a distributed ledger that is accessible to all participants. This transparent nature of blockchain ensures that every transaction is verifiable, providing a high degree of trust and reducing the potential for fraud.
Additionally, blockchain technology introduces an extra layer of security to digital transactions, protecting against tampering, manipulation, and unauthorized access. The cryptographic techniques employed in blockchain ensure that transaction data remains secure and that the integrity of the assets being transferred is maintained. This security aspect closely aligns with physical transactions, where measures such as seals, signatures, and secure vaults are used to protect physical assets.
Moreover, blockchain technology enables the digitization of a wide range of financial assets, including stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities. These assets can be tokenized, representing their ownership or value digitally. This tokenization allows for fractional ownership, increased liquidity, and the ability to trade assets in a highly efficient and transparent manner.
In conclusion, the analogy between blockchain technology and the transfer of assets in the physical world is evident through its elimination of intermediaries, introduction of smart contracts, and provision of security and transparency.
Blockchain revolutionizes financial transactions by offering direct peer-to-peer transfers, streamlined processes, and enhanced trust, much like physical transactions in the traditional financial system. As blockchain continues to evolve, its impact on financial services will continue to be profound, transforming the way we manage and transact with assets in the digital world.

Case Study: Peer-to-Peer Blockchain Systems in Financial Services Industry
In the financial services industry, blockchain technology is revolutionizing traditional financial systems by enabling peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a trusted third party. This case study explores a use case where a token in a blockchain serves as a medium of exchange, store of value, and unit of account.
By leveraging the decentralized nature of blockchain, this case study demonstrates how traditional financial services can be implemented on a secure and transparent peer-to-peer blockchain system, offering increased security and efficiency compared to centralized systems:
Token Creation and Distribution:
A financial institution creates a token on a blockchain network, representing a digital asset that can be used as a medium of exchange, store of value, and unit of account. The tokens are distributed to participants through a transparent and auditable process, ensuring fairness and inclusivity.
Peer-to-Peer Transactions:
Using a digital wallet, individuals can securely and directly transact with each other using the token as the medium of exchange. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, such as banks or payment processors, reducing transaction costs and increasing transaction speed.
Secure and Transparent Ledger:
Transactions are recorded on the blockchain, creating an immutable and transparent ledger accessible to all participants. This enhances trust and accountability, as anyone can verify and audit transactions, ensuring the integrity of the financial system.
Smart Contract Automation:
Smart contracts, self-executing agreements written on the blockchain, enable the automation of financial services. For example, lending and borrowing can be facilitated through smart contracts, eliminating the need for traditional intermediaries like banks. The terms of the agreement, including interest rates and repayment schedules, are automatically enforced, providing security and efficiency.
Decentralized Identity and KYC:
Blockchain enables the development of decentralized identity solutions, where individuals can have control over their personal information. Know Your Customer (KYC) processes can be securely implemented on the blockchain, reducing the need for multiple identity verifications and enhancing privacy.
Asset Tokenization:
Blockchain allows for the tokenization of real-world assets, such as real estate or investment funds. These tokenized assets can be traded and divided into fractional ownership, unlocking liquidity and democratizing access to investment opportunities.
Enhanced Security and Trust:
Blockchain’s cryptographic features ensure the security and integrity of financial transactions. With decentralized consensus mechanisms, the risk of fraud and tampering is significantly reduced, providing users with increased trust in the system.
Global Accessibility and Inclusion:
Peer-to-peer blockchain systems have the potential to reach the unbanked and underbanked populations globally. With access to a smartphone and an internet connection, individuals can participate in the financial system, promoting financial inclusion and economic empowerment.
By leveraging the capabilities of blockchain technology, traditional financial services can be transformed into peer-to-peer systems, eliminating the need for trusted third parties. This case study highlights the benefits of implementing financial services on a secure and transparent blockchain network, offering increased security, efficiency, and accessibility. As blockchain adoption continues to grow, the financial services industry has the opportunity to reshape the way value is conveyed, empowering individuals and fostering a more inclusive and decentralized financial ecosystem.
Transforming Healthcare with Blockchain: Enhancing Data Security and Interoperability
In the healthcare sector, blockchain technology is driving significant transformations in data security and interoperability, much like the importance of privacy and data sharing in the physical world of healthcare. Just as patients value the confidentiality of their medical information and the ability to share it securely, blockchain offers a robust solution to address these concerns in the digital realm.
One of the key advantages of blockchain in healthcare is its ability to ensure the privacy and security of patient data. Medical records stored on the blockchain can be encrypted and accessed only by authorized individuals, preventing unauthorized access and maintaining the confidentiality of sensitive information. This level of security is analogous to physical healthcare records that are safeguarded in locked cabinets or secure facilities, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to them.
Moreover, blockchain enables patients to have greater control over their medical records. In the physical world, patients often carry their medical records from one healthcare provider to another, ensuring continuity of care. With blockchain, patients can securely store their medical data on the distributed ledger, granting them ownership and control over their records. This puts patients at the center of their healthcare journey, allowing them to share their data with healthcare providers as needed, ensuring accurate diagnoses, and facilitating personalized treatment plans.
The interoperability of healthcare data is another area where blockchain technology shines. In the physical world, the exchange of patient data between different healthcare providers can be challenging and time-consuming. Blockchain facilitates the seamless exchange of medical data between healthcare organizations, enabling efficient and secure data sharing. This interoperability ensures that healthcare providers have access to comprehensive patient information, leading to improved coordination of care and better patient outcomes.
Additionally, blockchain technology can enhance research and development in the healthcare industry. By securely and transparently sharing data on the blockchain, researchers can access a broader range of medical information while maintaining privacy and complying with ethical guidelines. This analogy aligns with the physical world, where research collaborations and data sharing are essential for advancing medical knowledge and discovering new treatments.
In conclusion, the analogy between blockchain technology and the transfer of assets in the physical world is evident in the healthcare sector’s transformation. Blockchain provides secure data storage, patient control over medical records, seamless data interoperability, and the potential to advance medical research. As blockchain continues to be integrated into healthcare systems, its impact on data security and interoperability will revolutionize the way healthcare is delivered, mirroring the importance of privacy and data sharing in the physical world of healthcare.
Supply Chain Transparency: Leveraging Blockchain for Traceability and Accountability
Blockchain technology serves as a powerful tool for achieving supply chain transparency, reflecting the need for traceability and accountability in the physical supply chain. In the physical world, ensuring that products are sourced ethically, manufactured under appropriate conditions, and meet regulatory standards is of paramount importance. Blockchain facilitates this by recording every step of a product’s journey on an immutable and transparent ledger.
Through blockchain, each stage of the supply chain, from sourcing raw materials to manufacturing, distribution, and sale, can be documented and verified. This creates a comprehensive and auditable record of a product’s history, similar to the paper trail that accompanies physical products. Consumers, businesses, and regulatory bodies can access this information, ensuring that the product’s origin and authenticity can be reliably verified.
One of the key benefits of blockchain in the supply chain is the ability to trace the provenance of goods. By linking each transaction and event to a specific product, blockchain enables end-to-end traceability. For instance, in the food industry, blockchain can track the journey of ingredients, ensuring their quality, authenticity, and adherence to safety regulations. Consumers can scan a product’s QR code or access its unique identifier to view the blockchain records, offering them confidence in the product’s integrity, similar to how physical products are accompanied by labels and certifications.
Blockchain also promotes accountability throughout the supply chain. Every participant involved in the supply chain, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers, can record and verify their actions on the blockchain. This creates a decentralized and transparent ecosystem where each party is accountable for their contributions. By analogy, just as physical supply chains rely on contractual agreements, quality control measures, and audits to ensure accountability, blockchain establishes a digital infrastructure that enhances trust and enables efficient collaboration among supply chain participants.
Furthermore, blockchain technology enhances supply chain resilience by reducing the risk of counterfeit products. Counterfeit goods pose significant challenges across industries, compromising consumer safety, brand reputation, and revenue. Through the use of blockchain, the provenance and authenticity of products can be easily verified, deterring counterfeiters and protecting consumers. Manufacturers can assign unique identifiers or digital certificates to their products, which can be securely recorded on the blockchain. This helps consumers differentiate genuine products from counterfeit ones, offering a level of assurance that is akin to physical product authentication measures.
In conclusion, the analogy between blockchain technology and the transfer of assets in the physical world is evident in the context of supply chain transparency. Blockchain enables full traceability and accountability, similar to the need for transparency and traceability in the physical supply chain. By recording and verifying every step of a product’s journey on the blockchain, it becomes possible to ensure ethical sourcing, proper manufacturing conditions, compliance with regulations, and the ability for consumers to verify product authenticity. As blockchain continues to be adopted in supply chain management, it will revolutionize the way products are tracked, verified, and exchanged, bringing increased transparency and trust to the global supply chain.

Case study : Combining the Blockchain and IoT technologies
One compelling example of combining blockchain and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies within the supply chain industry is in the context of shipping goods. This integration can bring transparency, efficiency, and security to the shipping process, benefiting all stakeholders involved.
Imagine a scenario where a company is shipping a container of goods internationally. By leveraging IoT devices, the company can track and monitor various aspects of the shipping process, such as location, temperature, humidity, and container integrity. These IoT devices can be embedded within the containers, providing real-time data that is collected and transmitted securely.
Now, here’s where blockchain technology comes into play. The data collected from the IoT devices can be recorded on a blockchain, creating an immutable and transparent ledger of information. Each data point, such as the container’s location at a specific time, the temperature variations during transit, or any incidents affecting the container, can be securely stored on the blockchain.
This integration offers several benefits. Firstly, it enhances transparency by providing all stakeholders, including the shipper, recipient, and any intermediaries, with real-time access to the container’s status and conditions. This transparency reduces information asymmetry and eliminates the need for manual tracking and communication, leading to improved efficiency in the supply chain.
Secondly, the combination of blockchain and IoT enhances the security of the shipping process. Any tampering or unauthorized access to the container can be detected through the IoT sensors, and this information can be immediately recorded on the blockchain. The decentralized and immutable nature of the blockchain ensures that the data cannot be altered or manipulated, providing an auditable trail of events. This feature is particularly crucial in mitigating the risks of theft, fraud, or counterfeit goods within the supply chain.
Furthermore, the integration of blockchain and IoT enables automated and smart contract-based processes. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements that automatically trigger actions when predefined conditions are met. In the context of shipping goods, smart contracts can be utilized to automate various tasks, such as releasing payment to the supplier once the goods are received and verified by the recipient. This automation reduces the need for intermediaries, streamlines the payment process, and eliminates potential disputes.
Overall, combining blockchain and IoT technologies within the supply chain industry, specifically in the shipping of goods, brings numerous advantages. It offers transparency, efficiency, and security by leveraging IoT devices to collect real-time data and recording it on an immutable blockchain. This integration enables stakeholders to track the progress of shipments, ensures the integrity of goods, and automates processes through smart contracts. As a result, the shipping industry can benefit from enhanced supply chain management, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
The Retail Revolution: Blockchain’s Influence on Customer Trust and Product Authentication
In the retail industry, blockchain technology is making significant strides in fostering customer trust and product authentication, aligning with the fundamental need for trust and authentication in physical retail transactions. The use of blockchain enables retailers to establish an immutable and tamper-proof record of a product’s history, encompassing vital information such as its origin, manufacturing processes, and supply chain journey. By doing so, retailers can provide customers with an unprecedented level of transparency and assurance.
When customers encounter a product with a blockchain-based identifier, they can use their smartphones or other devices to scan it and access the product’s unique blockchain record. This record acts as a digital passport, verifying the product’s authenticity and providing a comprehensive overview of its entire lifecycle. Customers can delve into the details of where the product was sourced, how it was manufactured, and how it traveled through the supply chain, creating a sense of trust and transparency that mirrors the physical world’s examination of labels, packaging, and other tangible attributes.
Through this blockchain-enabled authentication process, customers can confidently verify that the product they are purchasing is genuine. This is particularly crucial in sectors plagued by counterfeit goods, such as luxury fashion, electronics, and pharmaceuticals. Just as customers in physical retail settings scrutinize product labels, holograms, and other security features to validate authenticity, blockchain technology empowers customers to make informed purchasing decisions by ensuring the integrity of the product they are buying.
Furthermore, blockchain technology can enhance customer trust by addressing concerns related to ethical sourcing and sustainability. With increasing consumer demand for environmentally friendly and socially responsible products, blockchain can provide visibility into a product’s supply chain, showcasing the steps taken to ensure ethical practices, fair labor conditions, and adherence to sustainability standards. Customers can verify the claims made by retailers and make conscious choices that align with their values, much like how physical retail transactions involve selecting products with certifications and labels that signify ethical and sustainable practices.
The analogy between blockchain technology and the transfer of assets in the physical world is evident in the retail industry’s context. Just as physical retail transactions rely on visible indicators of authenticity and trust, such as product packaging, labels, and security features, blockchain enables a digital infrastructure that instills similar confidence in customers. By leveraging blockchain, retailers bridge the gap between the physical and digital realms, offering a seamless and secure way to authenticate products and build trust in an increasingly globalized and complex retail landscape.
Ultimately, the adoption of blockchain technology in the retail industry revolutionizes customer trust and product authentication. It brings transparency to the forefront, allowing customers to make informed choices by accessing detailed information about a product’s origin, manufacturing processes, and supply chain journey. This level of transparency not only assures customers of a product’s authenticity but also fosters a sense of trust and confidence in the retailer. As blockchain continues to shape the retail industry, it propels the transfer of assets in the digital world closer to the seamless, trust-based experience customers have come to expect in physical retail transactions.

Case Study : Digital Twin Integration in a Retail Store with Enhanced User Experience
In the retail industry, blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way customers interact with products, enhancing their user experience and providing a range of additional services. One such use case is the implementation of digital twins, which are digital representations of physical goods. This case study explores how a retail store leverages blockchain technology to create a seamless transition from the physical world to the digital realm, offering customers a host of interactive services and opportunities to engage with their purchased products.
Below the details of such eXperience:
Customer Purchase:
A customer visits a retail store and purchases a product, such as a high-end electronic device. Along with the physical product, the customer receives a unique digital identifier linked to a blockchain-based digital twin. This digital twin serves as a virtual representation of the physical product, stored securely on the blockchain.
Access to Digital Twin:
The customer gains access to the digital twin through a mobile application or an online platform. This digital twin provides a range of services and features that enable the customer to interact with the product as if it were in the real world.
Enhanced User Experience:
Through the digital twin, the customer can explore detailed product specifications, user manuals, and instructional videos. They can customize settings, control features remotely, and receive real-time updates and notifications related to the product.
Additional Services:
The digital twin platform offers the customer opportunities to purchase additional services and accessories related to the product. For example, they can buy extended warranties, subscribe to maintenance and repair services, or access exclusive content and updates. These services enhance the value proposition and engagement for the customer beyond the initial purchase.
Track Provenance and Authenticity:
Blockchain technology ensures the authenticity and provenance of the product. The digital twin provides a transparent record of the product’s origin, manufacturing process, and supply chain journey. Customers can verify the authenticity of their product and trace its entire lifecycle, fostering trust and confidence in their purchase.
Community and Social Interaction:
The digital twin platform facilitates social interaction among customers who own the same product. Users can join communities, share experiences, exchange tips, and even engage in peer-to-peer trading of digital assets associated with the product. This fosters a sense of belonging and creates a vibrant ecosystem around the product.
Data-driven Insights:
The digital twin captures valuable data about customer usage patterns, preferences, and feedback. Retailers can analyze this data to gain insights into customer behavior, product performance, and market trends. This data-driven approach helps retailers optimize their offerings, personalize recommendations, and improve overall customer satisfaction.
By integrating blockchain technology and digital twins, retailers can transform the user experience and extend it beyond the physical transaction. Customers can access a digital representation of their purchased goods, unlocking a plethora of interactive services, track provenance, and engage with a vibrant community. This case study demonstrates how blockchain is revolutionizing the retail industry, enhancing customer engagement, fostering trust, and creating new business opportunities. As blockchain adoption continues to grow, the retail sector is poised to witness further innovations that reshape the way we interact with products in the digital realm.
Blockchain in the Food Industry: Ensuring Safety, Traceability, and Ethical Sourcing
Within the food industry, blockchain technology is rapidly transforming the way safety, traceability, and ethical sourcing are ensured, much like their significance in the physical world of food production. Through the use of blockchain, every stage of the food supply chain, from the sourcing of ingredients to processing and distribution, can be recorded and made transparent, allowing for complete traceability of food products.
Just as consumers rely on physical indicators such as product labels, certifications, and expiration dates to assess the quality and safety of food, blockchain technology empowers consumers to access a digital ledger that captures comprehensive information about the food they consume. By scanning a product’s unique blockchain identifier, consumers can verify its origin, the farms or producers involved, as well as the processes it has undergone throughout the supply chain. This transparency provides an analogous experience to examining physical attributes in the world of food, instilling confidence in the safety and authenticity of the products they choose.
The application of blockchain in the food industry has far-reaching benefits. Firstly, it aids in the identification and containment of foodborne illnesses. In the event of a food safety issue, blockchain enables swift and accurate traceability, allowing authorities to pinpoint the source of contamination and take immediate action. By having a transparent record of the food’s journey, blockchain technology enhances food safety protocols, protecting consumers from potential health risks and facilitating more effective recalls, similar to how physical recalls are carried out to prevent harm.
Additionally, blockchain technology addresses the issue of food fraud, which is prevalent in various forms, such as mislabeling, adulteration, and counterfeiting. By recording the entire supply chain on the blockchain, from the source of ingredients to processing and distribution, any attempts to manipulate or falsify information become significantly more challenging. Consumers can verify the authenticity and quality of the food they purchase by accessing the blockchain records, creating a level of trust and accountability that parallels the physical world’s reliance on genuine labeling and certification processes.
Moreover, blockchain technology reinforces ethical sourcing practices within the food industry. Consumers are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact, labor conditions, and sustainability of their food choices. Blockchain enables transparent documentation of these aspects, allowing consumers to verify claims made by food producers regarding responsible sourcing and fair trade practices. This empowers consumers to make informed decisions, aligning their values with their food choices, much like how they seek labels and certifications in the physical world that demonstrate ethical sourcing and sustainability practices.
The analogy between blockchain technology and the transfer of assets in the physical world is evident in the food industry’s context. Just as physical food transactions require trust in the supply chain and rely on visible indicators of safety and authenticity, blockchain technology ensures the same trust and transparency in the digital realm. By leveraging blockchain, the food industry enhances safety, traceability, and ethical sourcing, providing consumers with the confidence that the food they consume aligns with their expectations and values.
In conclusion, blockchain technology plays a pivotal role in the food industry by ensuring safety, traceability, and ethical sourcing. Its application enables complete transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain, empowering consumers to verify the quality, authenticity, and ethical practices associated with the food they consume. By leveraging blockchain, the food industry bridges the gap between the physical and digital worlds, bringing the transfer of assets in the digital realm closer to the trusted experience consumers expect in the physical world of food production.
Overcoming Challenges: Scaling Blockchain for Mass Adoption in the Age of Avatar
While the potential of blockchain technology is vast, it faces challenges that must be overcome for widespread adoption, reminiscent of the challenges encountered in the physical world. One of the primary hurdles is scalability, as existing blockchain architectures may have limitations in handling a large number of transactions. Similar to the physical world, where there are constraints on the capacity of infrastructure, blockchain networks must find ways to scale effectively.
To address scalability challenges, ongoing research and development efforts are underway to explore innovative solutions. Layer-two scaling solutions, such as the Lightning Network for Bitcoin, aim to enhance transaction throughput by processing transactions off-chain while still maintaining the security provided by the underlying blockchain. Sharding is another promising approach that involves dividing the blockchain network into smaller, more manageable parts called shards, allowing for parallel processing of transactions. These advancements in scalability will enable blockchain technology to handle a significantly larger volume of transactions, mirroring the ability of physical systems to accommodate a high volume of transactions.
Furthermore, regulatory considerations are crucial for the widespread adoption of blockchain technology, just as regulations govern transactions in the physical world. Governments and regulatory bodies recognize the importance of striking a balance between fostering innovation and safeguarding consumers’ interests. They are actively working on establishing frameworks that facilitate the responsible and secure use of blockchain technology. This entails defining standards for data protection, privacy, and financial transactions, similar to how regulations and policies are in place in the physical world to ensure fair and secure transactions.
Regulatory frameworks provide assurance to users and businesses operating within the blockchain ecosystem. They serve as a bridge between the physical and digital realms, ensuring that blockchain-based transactions adhere to legal requirements and protect individuals’ rights. By addressing regulatory concerns, blockchain technology can gain wider acceptance and trust, just as the physical world relies on regulatory oversight to maintain the integrity and fairness of transactions.
Moreover, as blockchain technology continues to evolve and mature, collaborations between industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies become vital. This partnership allows for a comprehensive understanding of the technology’s potential, risks, and implications. It also enables the development of regulatory frameworks that foster innovation while mitigating potential risks associated with blockchain-based transactions. The process of establishing such regulations mirrors the collective efforts in the physical world to create a secure and regulated environment for conducting transactions.
In conclusion, while blockchain technology holds immense promise, its adoption on a mass scale faces challenges similar to those encountered in the physical world. Scalability limitations and regulatory considerations are key areas that need to be addressed. However, ongoing research and development efforts are exploring solutions to enhance scalability, and regulatory frameworks are being developed to strike a balance between innovation and consumer protection. By addressing these challenges, blockchain technology can overcome the barriers to adoption and achieve its full potential, much like the physical world has established regulations and systems to facilitate secure and fair transactions.
The Future of Blockchain: Exploring the Potential for Tokenization and Decentralized Economies
As we look ahead, the future of blockchain technology holds immense potential for tokenization and the emergence of decentralized economies, drawing parallels to the way physical assets and economies function. Tokenization, the process of representing real-world assets as digital tokens on the blockchain, opens up a world of possibilities. It allows for fractional ownership, increased liquidity, and democratized access to investment opportunities that were previously restricted to a select few. This transformative aspect of blockchain mirrors the way physical assets are divided, traded, and invested in the real world.
By tokenizing assets, individuals can own fractions of valuable assets such as real estate, art, or even intellectual property. These digital tokens can be bought, sold, and traded on blockchain-based platforms, enabling greater market efficiency and accessibility. Just as physical assets can be divided into shares or units, tokenization allows for the fractional ownership of assets, breaking down barriers and enabling participation in previously exclusive markets.
Moreover, blockchain technology enables the development of decentralized applications (DApps) and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). DApps are software applications that run on a decentralized network of computers, making them resistant to censorship and tampering. They provide users with direct access to services, removing the need for intermediaries. DAOs take decentralization a step further by establishing governance models that are transparent and democratic. Decision-making and governance in DAOs are distributed among network participants, giving individuals greater control over their assets and the power to shape economic systems.
This decentralized approach to governance and decision-making aligns with the analogies we find in the physical world. In physical transactions, individuals have the freedom to make decisions, exchange goods and services, and participate in economic systems. Similarly, blockchain technology empowers individuals by removing the reliance on centralized authorities and intermediaries. It shifts the power dynamics and allows for a more inclusive and participatory economy.
The analogy between blockchain technology and the transfer of assets in the physical world goes beyond mere technical innovation. It reflects a shift in our understanding of trust, transparency, and the way economic systems are designed. In the Age of Avatar, where the digital and physical worlds converge, blockchain technology acts as a catalyst for this transformation. It empowers individuals with greater control over their assets, enhances security and transparency in transactions, and unlocks new possibilities for innovation and economic models.
As we embrace this paradigm shift, it is crucial to navigate the challenges that lie ahead. Scalability, regulatory frameworks, and education are key areas that need attention. Scaling blockchain networks to handle a massive volume of transactions, creating regulatory frameworks that foster innovation and protect users, and educating individuals about the potential of blockchain technology are critical steps in realizing its full potential.
In conclusion, the analogy between blockchain technology and the transfer of assets in the physical world helps us understand the transformative power of blockchain in digitizing the physical world. Tokenization, decentralized applications, and decentralized autonomous organizations are revolutionizing the way we own, trade, and govern assets. By embracing these innovations, we can shape a future where individuals have greater control over their assets, trust and transparency are fundamental, and economic systems are more inclusive and participatory. In the Age of Avatar, blockchain technology is at the forefront, leading us into a new era of possibilities and reshaping the way we interact with the physical world.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology represents a groundbreaking solution for digitizing the physical world. Through its ability to provide secure, transparent, and efficient transactions, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize industries such as supply chain, healthcare, finance, retail, and more. By leveraging the analogy between blockchain technology and the transfer of assets in the physical world, we can understand its transformative power. From enhancing supply chain transparency and streamlining real estate transactions to enabling secure digital identities and revolutionizing payment systems, blockchain offers immense possibilities. As we continue to explore and harness the capabilities of blockchain technology, we are witnessing a paradigm shift in the design of economic systems. The age of Avatar is upon us, where the physical world merges seamlessly with the digital realm, empowered by blockchain technology. It is an exciting time for tech enthusiasts and forward-thinking individuals, as we unlock the full potential of blockchain to create a more secure, transparent, and interconnected future. So, let us embrace this technology and embark on a journey towards a digitized, blockchain-powered world.
FAQ
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. It enables secure and transparent peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries.
How does blockchain technology help to digitize the physical world?
Blockchain technology helps digitize the physical world by providing a secure and transparent platform to record and verify transactions, assets, and information. It enables the transfer and tracking of physical assets in a digital format, enhancing transparency, efficiency, and trust.
What are the advantages of using blockchain over traditional transaction methods?
Blockchain offers advantages such as enhanced security through cryptography, transparency through decentralized record-keeping, reduced reliance on intermediaries, increased efficiency in transaction settlement, and the potential for immutable and tamper-proof records.
How does blockchain ensure the authenticity and integrity of digital assets?
Blockchain uses cryptographic algorithms to create digital signatures and hash functions that verify the authenticity and integrity of digital assets. Once recorded on the blockchain, the information cannot be altered without consensus from the network participants, ensuring data immutability.
Can blockchain technology be applied to industries other than finance?
Yes, blockchain technology can be applied to various industries, including supply chain, healthcare, retail, real estate, energy, and more. It offers benefits such as enhanced traceability, improved transparency, streamlined processes, and secure data sharing.
What are some real-world examples of blockchain implementation in different industries?
Examples include Walmart and IBM’s Food Trust for supply chain transparency, SelfKey for digital identity verification, Propy for digitizing real estate transactions, and various initiatives for peer-to-peer energy trading and decentralized healthcare record systems.
How does blockchain technology address security concerns?
Blockchain ensures security through its decentralized and cryptographic nature. Transactions are verified by network participants, and once recorded on the blockchain, they are resistant to tampering or fraud. Additionally, encryption techniques protect sensitive data, enhancing security.
What are the challenges associated with blockchain adoption in the physical world?
Challenges include scalability to handle large transaction volumes, regulatory compliance, interoperability with existing systems, and educating users about the benefits and usage of blockchain technology. Overcoming these challenges requires collaboration and ongoing development efforts.
Is blockchain technology suitable for small businesses and individuals?
Yes, blockchain technology is not limited to large enterprises. It offers benefits to small businesses and individuals, such as cost savings, enhanced security, and opportunities for decentralized applications and peer-to-peer transactions.
How does blockchain technology impact economic systems?
Blockchain technology introduces a paradigm shift in economic systems by enabling decentralized and trustless transactions. It allows for the tokenization of assets, fractional ownership, and the emergence of decentralized economies, giving individuals greater control over their assets and participation in economic decision-making.
Sources
- Tapscott, D., & Tapscott, A. (2016). Blockchain revolution: how the technology behind bitcoin is changing money, business, and the world. Penguin.
- Swan, M. (2015). Blockchain: Blueprint for a new economy. “O’Reilly Media, Inc.”.
- Nakamoto, S. (2008). Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system. Retrieved from https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
- Chen, L., Xu, L., & Zhang, Y. (2018). Blockchain-based supply chain finance: a systemic risk perspective. Sustainability, 10(4), 1072.
- Deloitte Insights. (2021). Blockchain in health and life insurance: A distributed future for the insurance industry. Retrieved from https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/financial-services/blockchain-in-insurance.html
- World Economic Forum. (2019). Blockchain beyond the hype: A practical framework for business leaders. Retrieved from http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Blockchain_Beyond_the_Hype_Report_2018.pdf
- IBM. (n.d.). IBM Food Trust. Retrieved from https://www.ibm.com/food/
- SelfKey. (n.d.). SelfKey — Digital Identity Network. Retrieved from https://selfkey.org/
- Propy. (n.d.). Propy — The Decentralized Property Store. Retrieved from https://propy.com/
- Stahl, F., Langer, L., & Siering, M. (2018). Token-based business models: An introduction to the blockchain technology. Business & Information Systems Engineering, 60(4), 377–381.

Sami Belhadj is an experienced IT professional with over 20 years of experience in software development and IT operations. He has a strong background in DevOps, SRE, and Innovation, and is passionate about leveraging technology to drive business growth and innovation.He is a prolific writer and blogger, with a focus on topics related to Innovation and emerging technologies. In his free time, Sami enjoys exploring new technologies and Hiking.
Originally published at https://www.linkedin.com.
