Blockchain technology has transformed various industries by providing decentralized, secure, and transparent systems. Yet, as this technology evolves, it grows more complex, introducing new layers to enhance its functionality. For IT engineers, entrepreneurs, and Web3 experts, staying updated on these advancements is vital to unlocking blockchain’s full potential. In this article, we’ll simplify the concept of Layer 3 (L3) blockchains, the newest innovation aiming to elevate blockchain technology.
We’ll start by explaining how Layer 3 compares to the more familiar Layer 1 (L1) and Layer 2 (L2) structures, using simple analogies to make the layered architecture accessible to everyone. Then, we’ll break down the technical aspects of how L3 works. Real-world applications and case studies will help illustrate the success of L3 implementations. Finally, we’ll explore how L3 could drive mass adoption of blockchain and its potential to revolutionize industries.
The Layered Architecture of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is built in layers, with each one adding new functionality. This layered design is essential for handling the challenges of scalability, security, and usability in blockchain applications. Let’s break down the different layers—starting with Layer 0, which often flies under the radar—and see how they all interact.
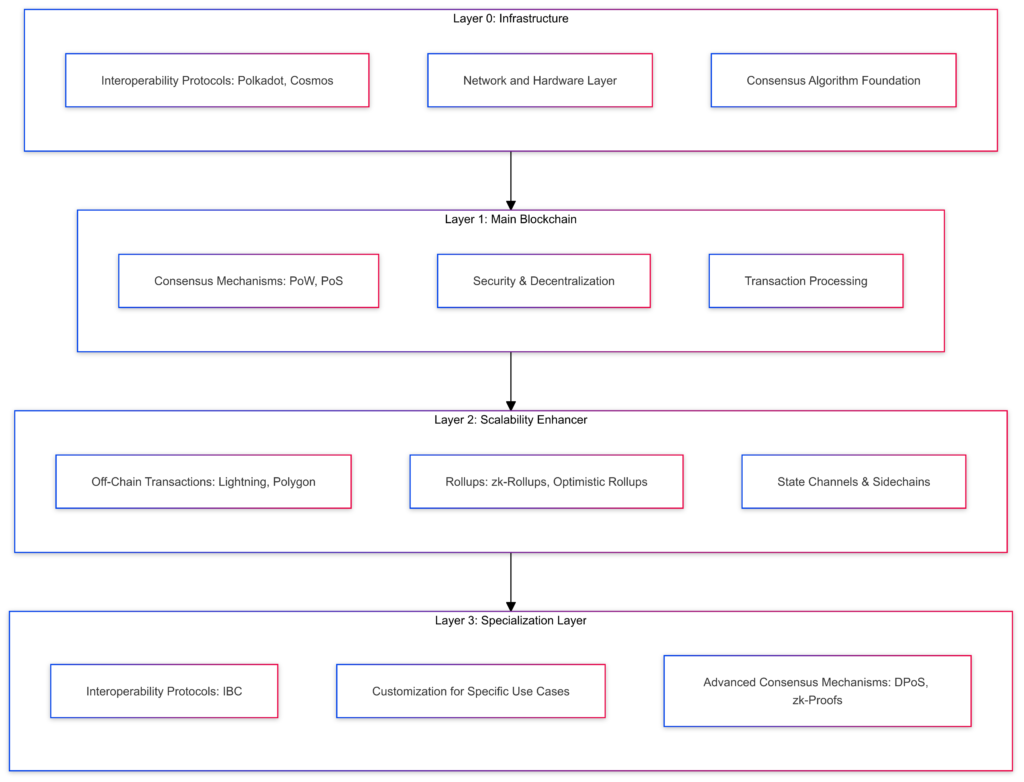
Layer 0: The Underlying Infrastructure
Layer 0 is the foundation of the blockchain system, providing the necessary infrastructure for other layers to function. It includes:
- Interoperability Protocols: Frameworks like Polkadot and Cosmos allow multiple blockchains to communicate with each other through protocols like Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) and Polkadot’s relay chains.
- Network and Hardware Layer: This is the physical layer of nodes and network connections that make blockchain networks run. It ensures secure data exchange and robust infrastructure support.
- Consensus Algorithm Foundation: Different Layer 1 blockchains rely on various consensus algorithms, and Layer 0 makes sure these protocols run efficiently and securely.
Layer 1: The Foundation
Layer 1 blockchains are what most people think of when they hear “blockchain.” These are the mainnets—like Bitcoin and Ethereum—where transactions are directly processed. Key features include:
- Consensus Mechanisms: L1 blockchains use consensus algorithms like Proof of Work (PoW), which involves solving complex problems (used by Bitcoin), and Proof of Stake (PoS), where validators stake tokens (used by Ethereum 2.0) to verify transactions.
- Security and Decentralization: L1 is designed to be highly secure and decentralized, with thousands of nodes ensuring the network remains safe and reliable.
- Transaction Processing: All transactions occur on-chain, which can lead to scalability issues as the network grows.
Layer 2: The Scalability Enhancer
Layer 2 solutions improve the scalability and efficiency of L1 blockchains by handling transactions off-chain and settling them later on the main blockchain. L2 features include:
- Off-Chain Transactions: Solutions like Lightning Network (for Bitcoin) and Polygon (for Ethereum) reduce congestion and fees by processing transactions off the main blockchain.
- Rollups: Technologies like zk-Rollups and Optimistic Rollups bundle multiple transactions into one, reducing the load on L1.
- State Channels and Sidechains: These allow for faster, off-chain transactions, with only the final state recorded on L1.
Layer 3: The Specialization Layer
Layer 3 represents the application layer, where specialized features are built on top of L1 and L2 foundations. Here’s how L3 stands out:
- Interoperability: L3 solutions focus on enabling smooth communication between different blockchain networks. Protocols like IBC are critical for cross-chain transactions.
- Customization: L3 blockchains can be tailored for specific use cases, allowing developers to create specialized blockchains with features optimized for their needs.
- Advanced Consensus Mechanisms: L3 solutions often use modern algorithms like Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and cryptographic techniques like zero-knowledge proofs for enhanced security and efficiency.
Technical Breakdown: How Layer 3 Works
At its core, Layer 3 acts as the application layer, sitting atop the infrastructure provided by L1 and the scalability improvements of L2. Here’s a look under the hood:
- Interoperability Protocols: L3 enables seamless communication across blockchains through cross-chain bridges and protocols like IBC. This creates a more interconnected ecosystem.
- Advanced Consensus Algorithms: L3 blockchains often employ Proof of Stake (PoS) and Delegated PoS (DPoS) to maintain decentralization and security while optimizing performance.
- Efficient Transaction Processing: Techniques like zk-Rollups and Validium process transactions off-chain, improving efficiency while maintaining security.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases of Layer 3
L3 solutions are not just theoretical—they are already being implemented. Let’s explore some successful real-world applications:
Case Studies
- Arbitrum Orbit: Built on the Arbitrum Nitro platform, Arbitrum Orbit enables developers to create customized blockchains that are highly scalable and cost-effective, ideal for gaming and decentralized finance (DeFi).
- zkSync Hyperchains: These combine the speed and cross-chain capabilities of L3 with the settlement efficiency of L2, making them perfect for high-speed applications like NFT marketplaces.
- Orbs: This decentralized serverless cloud solution enhances smart contract execution and integrates seamlessly with L1 and L2 protocols.
How Layer 3 Differs from Other Layers
L3 blockchains bring unique features to the table, particularly when it comes to scalability, interoperability, and cost efficiency.
Scalability
While L1 struggles with scalability due to its focus on security and decentralization, L2 offers relief by processing transactions off-chain. However, L3 takes scalability further by providing specialized solutions that support high transaction throughput, making it ideal for use cases like gaming and DeFi.
Interoperability
L1 blockchains are often siloed, limiting interoperability. L2 solutions help a bit, but L3 truly excels, offering seamless communication across different blockchain networks, which is key for creating a connected ecosystem.
Cost Efficiency
L1 blockchains can be expensive during peak usage, while L2 reduces costs by moving transactions off-chain. L3 solutions, with their efficiency-driven designs, further slash costs, making them perfect for frequent, low-cost transactions.
Economic Models in Layer 3
Layer 3 blockchains are built for efficiency, and their economic models reflect this. By processing transactions off-chain and only settling them occasionally, L3 solutions drastically reduce transaction fees.
L3 also opens the door for new monetization strategies. Developers can implement customized fee structures or use tokenization to incentivize participation and create new revenue streams. Governance tokens allow communities to have a say in the operation of the blockchain, further decentralizing control.
Regulatory Landscape for Layer 3
As blockchain evolves, so too does the regulatory landscape. Governments are increasingly recognizing the need to regulate advanced technologies like L3. Compliance with laws such as the GDPR (European Union) and CCPA (California) is essential, and L3 solutions often incorporate advanced cryptography to meet these stringent requirements.
For instance, L3 blockchains use encryption techniques like fully homomorphic encryption to protect user data, ensuring that blockchain technology aligns with global data privacy laws.
How Layer 3 Drives Mass Adoption
Layer 3 has the potential to push blockchain technology into the mainstream by making it more accessible and user-friendly. Here’s how:
- Improved User Experience: Faster transactions and lower fees make L3 solutions more attractive for real-world applications, especially in areas like gaming and DeFi.
- Lower Barriers to Entry: By providing developers with the tools to create application-specific blockchains, L3 makes it easier to build blockchain-based solutions without needing to manage complex infrastructure.
- Innovative Applications: With L3, developers can create decentralized apps (DApps) that leverage advanced functionality like cross-chain interoperability and enhanced security, encouraging more innovation across industries.
A Glimpse into the Future of Layer 3
As L3 continues to evolve, it will likely integrate more deeply with traditional industries like finance, supply chain management, and healthcare. These sectors are starting to see the value in blockchain’s transparency and security, and L3 solutions provide the scalability and customization needed to support these industries.
At the same time, regulatory frameworks will adapt to accommodate blockchain technology, and L3 blockchains—with their built-in compliance capabilities—will be at the forefront of these developments.
Conclusion
Layer 3 blockchains represent a significant leap in blockchain technology. Building on the security of L1 and the scalability of L2, L3 offers unparalleled customization, interoperability, and efficiency. It addresses key challenges like cross-chain communication and cost reduction, making it a powerful addition to the blockchain ecosystem.
For IT engineers, L3 opens a new frontier of technical innovation, while entrepreneurs can leverage its features to build scalable, robust business solutions. Web3 experts will find that L3’s cross-chain capabilities pave the way for the next generation of decentralized applications, driving mass adoption and innovation.
In short, Layer 3 blockchains are poised to play a critical role in shaping the future of blockchain technology, making it more accessible, efficient, and ready for widespread adoption.
Sources:
- Polkadot Documentation
- Description: Detailed explanation of Polkadot’s interoperability protocols and how its relay chains function.
- URL: https://polkadot.network/technology/
- Cosmos Network Documentation
- Description: A comprehensive guide to Cosmos and the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol, focusing on cross-chain interoperability.
- URL: https://cosmos.network/
- Ethereum 2.0 Overview – CoinTelegraph
- Description: In-depth analysis of Ethereum’s transition from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS) and its implications for scalability and efficiency.
- URL: https://cointelegraph.com/ethereum-2.0
- zk-Rollups and Validium – ZK Sync Documentation
- Description: Technical details on zk-Rollups and Validium, focusing on how they enhance scalability while maintaining security.
- URL: https://docs.zksync.io/
- Layer 2 Solutions Explained – Antier Solutions
- Description: A comprehensive article detailing Layer 2 solutions such as Polygon and the Lightning Network, focusing on their scalability improvements.
- URL: https://www.antiersolutions.com/layer-2-blockchain-scaling-solutions/
- Orbs Network Documentation
- Description: Explanation of how Orbs functions as a decentralized, serverless cloud to enhance smart contract execution and integration with Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchains.
- URL: https://www.orbs.com/
- Arbitrum Official Documentation
- Description: In-depth explanation of how Arbitrum’s Nitro platform and Orbit solution work to enhance blockchain scalability and customization.
- URL: https://developer.arbitrum.io/
- Chainlink Documentation
- Description: Overview of Chainlink’s oracle services and how they support Layer 3 applications by integrating real-world data into blockchain smart contracts.
- URL: https://docs.chain.link/
- zkSync Hyperchains
- Description: Explanation of zkSync’s Hyperchains, which leverage Layer 2 solutions for fast cross-chain messaging and interoperability.
- URL: https://zksync.io/hyperchains
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- Description: Official documentation on the EU’s data privacy law, which is relevant when discussing Layer 3’s compliance with global data privacy regulations.
- URL: https://gdpr.eu/
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
- Description: Details on the CCPA, which governs data privacy regulations in the state of California, particularly relevant for blockchain applications.
- URL: https://oag.ca.gov/privacy/ccpa
- CoinGecko Layer 3 Blockchain Reports
- Description: Market and technical reports on Layer 3 blockchain applications, including economic models, tokenomics, and governance mechanisms.
- URL: https://www.coingecko.com/en
- Halborn Blockchain Security
- Description: Security guidelines and overviews of blockchain protocols, including advanced consensus mechanisms such as Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and zk-Rollups.
- URL: https://www.halborn.com/
